It may seem gross or dirty, but contrary to the belief, earwax is very important for your hearing health. Understand how to safely clean your ears, along with some interesting facts about earwax.
What is earwax?
Earwax, medically known as cerumen, is a substance naturally produced by our bodies within the outer ear.
Earwax contains oil and sweat blended with dead skin cells.
What’s the purpose of earwax?
Although the thought of earwax can sometimes make people cringe, it’s hard to believe that this substance produced in our ears can be so beneficial to ears’ health. However, it’s sticky, and the smell is precisely why an average amount of earwax is helpful.
- Earwax is a natural deterrent to prevent bacteria from entering the inner ear. Due to its sticky nature, it collects tiny debris that can find its way into our ear canal, similar to fly paper trapping insects.
- It acts as a lubricant and protective coating for your ear canal. Without earwax, your outer ear might become itchy, dry, and flaky, putting it at a higher risk of irritation and infection.
- Did you know? The smell of earwax keeps bugs away, while the stickiness traps those that might find their way inside your ear
Cleaning your ears, is it needed?
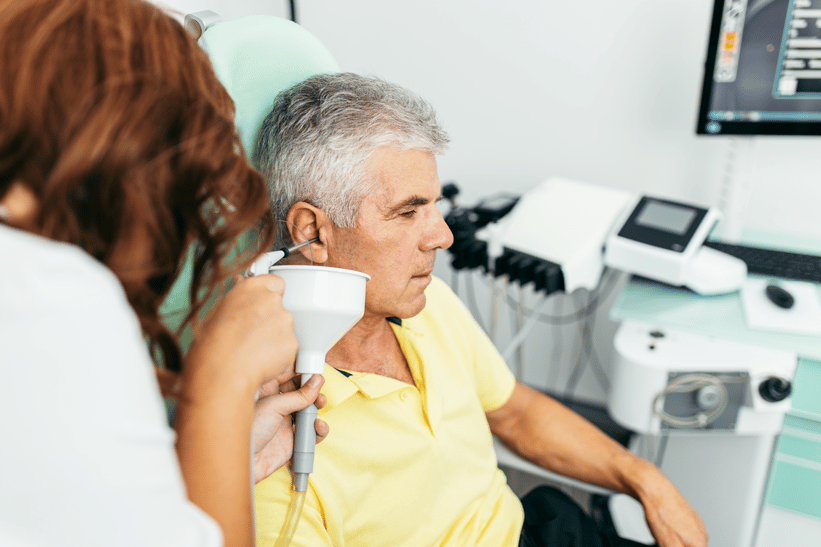
A recent article discussed the harms associated with not only cleaning your ears too often along with inserting objects into your ear. The report suggests that you can not only irritate, scratch, and or cut the ear canal, but you can also damage the eardrum. “People don’t realize the wax they see on a Q-tip would have come out anyway because the ear is “self-cleaning.”
Do you suspect impacted earwax?
If so, proceed with caution. Despite cerumen’s benefits, sometimes blockages can occur, notably if you tend to have dry, hard, impacted earwax. If you begin to experience a sense of fullness in your ears, feel like you are experiencing hearing loss, and suspect wax is the offender:
-
- Buy an over-the-counter ear cleaning kit if your ears are healthy. Ask a specialist for help if you have ear tubes or if you have any ear pain. Cerumen buildup should not be painful.
- Cleaning your hearing aids regularly or any other devices you insert into your ears.
Do not clean your ears with a cotton swab or any other type of instrument to remove wax on your own, and this can further push the wax into the ear canal, where it is incapable of being shed on its own naturally. You may even puncture your eardrum.
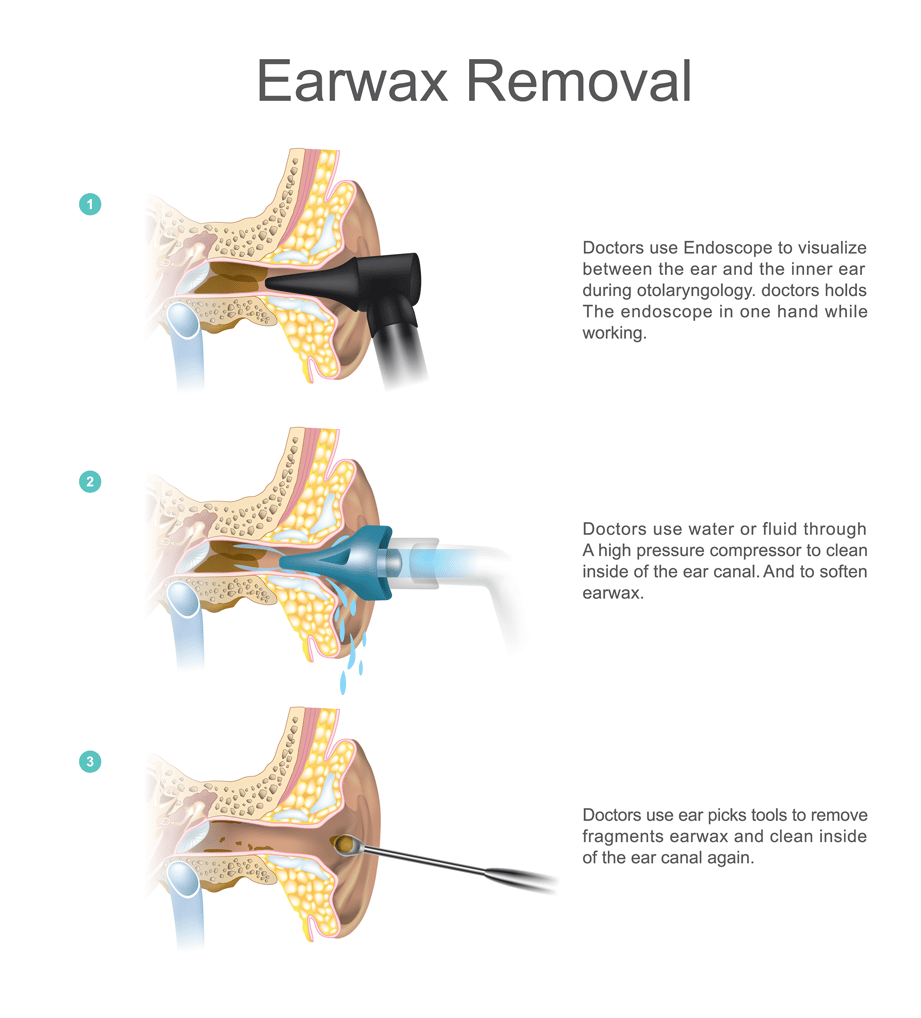
- Consider (in some cases) professional cleaning: Some hearing health providers offer professional cleaning, using specific tools like the Earigator. Most people do not need to use these services, but it’s easy for doctors to look in the ears using an otoscope to look for impacted earwax.
The more you clean and remove, the more your body will create
When you create a routine of removing earwax, it signals your body to make more, creating an overabundance that can impede your hearing and put you at greater risk for developing ear infections and other difficulties.
super-producers
Stress and fear can even accelerate earwax production. Others who have the disposition to produce too much earwax include those:
- Buy an over-the-counter ear cleaning kit if your ears are healthy. Ask a specialist for help if you have ear tubes or if you have any ear pain. Earwax buildup should not be painful.
- With a lot of hair in their ear canals.
- Who suffer from common ear infections.
- Who have abnormally-formed ear canals or osteomata, which is additional bone tissue.
- Who are older, have particular skin conditions, or have specific learning disabilities.
How much is too much?
Generally, your body knows exactly how much cerumen to make. If you maintain a healthy diet, have proper hygiene, and move your jaw (think chewing and talking), your ears will displace excess earwax, dirt, and debris without intervention
How to clean your ears
While your ears are self-cleaning, there are a few things you can do to keep them clean and free of excess debris:
- Clean your ears using a warm, soapy washcloth and allowing warm water from your everyday shower to run over (but not in) your ears. On occasion is likely enough to soften and loosen excess earwax.
- If you wear hearing aids, clean them appropriately and often.
- If you’re above 60, have your hearing evaluated periodically by a hearing healthcare professional. Ask your family physician for a referral, or search our online directory to find hearing clinics near you. Besides advising you on your hearing health, they will be able to detect excess cerumen and may safely remove it.
If you suspect any degree of hearing loss are are experiencing issues with earwax, call Salem Audiology Clinic today at (971)701-6322 and schedule an appointment with one of our highly trained Audiologists to assist you.
